Recently, Zheng Yu, a researcher at the Shenzhen Institute of Advanced Technology of the Chinese Academy of Sciences, and Hari Shroff, a professor at the National Institutes of Health, have successfully developed a novel two-photon excited super-resolution optical microscopy imaging system.

The system also has super-resolution optical microscopic imaging capabilities and large depth 3D imaging capabilities, enabling optical super-resolution imaging to advance to a record-breaking 250 micron. The corresponding research results are Adaptive optics improves multiphoton super-resolution imaging. Resolving microscopy has recently been published in Nature Methods.
“Looking fine†and “seeing deep†are two major challenges in the field of optical microscopy. After decades of unremitting efforts by researchers, both in terms of “seeing fine†and “seeing deep†A number of innovative technologies have emerged, and great success has been achieved, but optical microscopy imaging technologies with both “seeing fine†and “seeing deep†functions are rare.
In this study, Zheng et al. used two-photon microscopy (TPM) with deep biological imaging capabilities and transient structured illumination microscopy with super-resolution imaging (InstantStructured Illumination Microscopy). , ISIM) organically combine to achieve dual-photon excitation of super-resolution microscopy. At the same time, the researchers used Adaptive Optics (AO) technology to successfully overcome the wavefront phase distortion caused by biological tissue, and finally achieved 176 nm lateral resolution, 729 nm longitudinal resolution and 250 μm detection. Deep imaging effect. Using this technology, high-resolution three-dimensional imaging studies of cells, nematode embryos and larvae, Drosophila brain slices and zebrafish embryos can be performed, and the imaging effect is significantly better than the traditional two-photon imaging quality. It is worth mentioning that because this technology improves the photon utilization efficiency and thus reduces the required laser power, it can carry out long-term, high-definition three-dimensional dynamic observation of the development process of nematode embryos. This technique has no effect on the development of nematode embryos during up to 1 hour of continuous 3D imaging. This technique plays an important role in embryo development research.
The research was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China, the National Key Basic Research Development ("973") program, and the Shenzhen Overseas High-level Talent Innovation and Entrepreneurship Peacock Project.
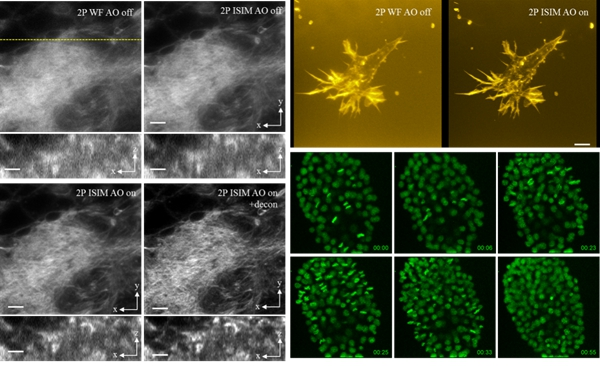
The left picture shows the comparison of the two-photon superimaging (2P ISIM) and two-photon super-resolution (2P ISIM AO) microscopy imaging of Drosophila brain slices in traditional two-photon imaging (2P WF), adaptive optics, upper right For the three-dimensional imaging comparison of cells located 150 microns deep in the collagen gel, it can be seen that the resolution of the new technology is significantly improved in both horizontal and vertical directions. The lower right panel shows the three-dimensional observation of the nematode embryo development for 1 hour. The normal cell division process proves that the technique can be used for embryonic development dynamics.
Edit review
This study combines two-photon microscopy imaging technology with the obvious microscopic imaging technology of homeopathic structure to achieve super-resolution microscopic imaging. At the same time, it improves photon utilization efficiency and helps to rapidly develop nematode embryo development. Imaging research is of great significance for embryo research in the biological field.
Medical Cart,Hospital Cart,Emergency Trolley,Medical Instrument Cart
Jiangmen Jia Mei Medical Products Co.,Ltd. , https://www.jmjiameimedical.com