Recently, the Ion Beam Plant Genetic Engineering Laboratory of the Institute of Technical Biology and Agricultural Engineering, Hefei Institute of Material Science, Chinese Academy of Sciences has made new discoveries in the study of the mechanism of heavy ion mutagenesis.
Compared with traditional gamma rays, heavy ions, due to their unique physical properties and special energy deposition methods in matter, have shown great application prospects in the field of life sciences, and have become the current radiation biology, radiology, radiology Research hotspots in therapeutics and other fields. As heavy ions travel through the material, there is a varying energy deposition distribution along their radiation tracks, which can lead to different biological effects. However, previous related studies were conducted at the cellular level, and the track distribution of the biological effects of heavy ion radiation at the individual level has not been reported.
The mechanism research group of the researcher Bianpo of the Ion Beam Plant Genetic Engineering Laboratory of the Institute of Technology and Biology and the laboratory of the researcher Li Wenjian of the Institute of Modern Physics designed a layered irradiation experiment using the small volume of Arabidopsis seeds The living body level simulates continuous biological tissues, and is irradiated in layers with 87.5 MeV / u carbon ions from top to bottom. The frequency of homologous recombination and the expression level of AtRAD54 gene were used as the end point of mutagenesis detection to study the distribution of biological effects on the track of heavy ion radiation.
It was found that the distribution of genetic and biological effects along the incident path of heavy ions is not consistent with the physical Bragg curve, and the distribution of biological effects at the end point of developmental science is basically consistent with the physical Bragg curve, which indicates that different biological processes affect heavy ion There are different reaction modes.
Interestingly, for each biological examination endpoint, different doses of radiation (5Gy and 30Gy) resulted in almost the same distribution of biological effects, indicating that the micro-track structure of heavy ion radiation plays a key role in the induction of biological effects. effect. In addition, the irradiated progeny also showed a certain distribution of radiation effects (homologous recombination frequency), indicating that heavy ion radiation also induced changes at the epigenetic level.
The above research has laid a good foundation for elucidating the internal mechanism of the biological effect of heavy ion radiation.
This research was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China and the Chinese Academy of Sciences' innovative project. The relevant research content has been accepted by the international mainstream journal of radiation biology, Mutation Research / Fundamental and Molecular Mechanisms of Mutagenesis.
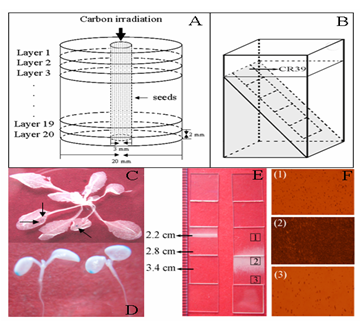
Schematic diagram of Arabidopsis thaliana irradiated by heavy ion
Distribution of homologous recombination frequency along the heavy ion tracks in irradiated contemporary (A) and progeny (B) individuals
BNF HARDWARE CO., LTD , https://www.bnfhardware.cn